In today’s world, every industry bears a responsibility to protect the environment, and it is no surprise that these responsibilities are increasing.
A 2023 analysis by ESG Book -a sustainability data provider – revealed a staggering 155% increase in global environmental, social and governance regulations over the past decade.
Industries operating underground, such as mining and civil infrastructure, face unique challenges due to sparse data and the complexities of the subsurface environment. From mines leaching contaminants to civil projects impacting groundwater levels or excavating contaminated soil, effective environmental management is essential.
But this isn’t just about fulfilling regulatory compliance or cost management. It’s about safeguarding our planet’s vital resources, meeting societal expectations, and navigating the ethical, reputational and even legal risks associated with environmental challenges.
Seequent’s software empowers governments, NGOs and environmental consultancies worldwide, to tackle some of our biggest environmental challenges through a deeper understanding of the underground. Our tools are trusted by seven of the top ten global environmental consultancies. As regulatory demands grow and climate instability increases, the global environmental consulting market is projected to expand by nearly 50% from 2022 ($45.6 billion) to 2027.
Dr Thomas D. Krom, Seequent’s Segment Director, Environment, notes a trend of consolidation within the environmental consultancy industry. He observes, “We are seeing an increasing number of mergers and acquisitions, driven by consultancies seeking to reduce costs and increase margins to satisfy investors, while also seeking to remain competitive and profitable in a rapidly changing industry.”
50%
The global environmental consulting market is projected to expand by nearly 50% from 2022 ($45.6 billion) to 2027
7/10
Seequent tools are trusted by seven of the top ten global environmental consultancies
73%
73% of individuals in the environmental industry consider data management to be of critical or high importance (Seequent’s 2023 Geoscience Data Management Survey)
Closing the skills gap through tech
Achieving efficiency in environmental projects has always been a significant challenge due to manpower shortages, uncertainties, and costs. Focusing on achieving the same or greater output using the same or fewer resources is a big part of the equation. Leveraging digital technologies and automation to improve efficiency is a cornerstone in achieving this goal.
Dr. Krom notes, “As staffing shortages in the industry are predicted to continue and the volume of work increases in a booming industry, a strategy where data is recognised as a significant asset together with technology that unlocks that data’s value can be transformational in delivering efficiencies.”
“By 2027, according to Environment Analyst’s market assessments and reports, it is expected that an additional 30-50% environmental staff will be required, but we are not training anywhere near that number.”
Modelling, data management and collaboration software, when used wisely and with a great user experience, allows environmental professionals to spend more time applying their expertise to solve problems rather than wasting time on repetitive tasks and cumbersome data management activities. It’s all about efficiency, effectively leveraging their experience, and empowering skilled subject matter experts through data and analysis, says Krom.
Restoring a vital water ecosystem in Brazil
In Brazil, the environmental services company Geoambiente S.A. used Seequent software to restore a vital water ecosystem at a sprawling 116,000-square-meter industrial complex. Decades of heavy-duty industrial processes were polluting the local area with harmful compounds, affecting local drinking water sources. The manufacturer hired Geoambiente to fix the issue, but the company couldn’t complete the job without understanding the source, entry point and extent of the pollution.
Geoambiente and Seeqent developed a digital hydrogeological model of the entire area to identify the source and extent of the pollution. The model converts complex data into clear, easy-to-interpret visualisations, enabling the placement of absorptive barriers in the most contaminated areas. Within six months, the solution significantly reduced contaminant levels, including a complete elimination of dichloroethylene and vinyl chloride, a 99% reduction in benzene levels and a 72% reduction in trichloroethylene. The result is cleaner aquifers and safer drinking water for local communities.
Dr Krom highlights: “Analyses can be updated quickly and intuitively accessed as more data becomes available, providing a common understanding of the subsurface conditions, enabling increased confidence in decision-making, mitigating mistakes, and facilitating the delivery of projects faster.”
Seequent’s tools facilitate effective communication of environmental project outcomes, making complex science accessible and improving decision-making.
Augmented reality helps visualise and communicate drinking water options
WSP developed a groundwater model to evaluate drinking water scenarios for 14 Minnesota communities contaminated with PFAS chemicals. The project’s complex geology, multiple stakeholders, and extensive data requirements presented challenges that previous software could not effectively address. WSP needed a comprehensive, collaborative 3D/4D solution to visualise and communicate subsurface hydrogeology.
WSP chose Leapfrog Works and Seequent Central for Hololens due to their detailed modelling, collaboration capabilities and interoperability with third-party applications. Working in a cloud-based modelling environment facilitated 4D application and mixed reality communication. This allowed all project participants and stakeholders to access 3D/4D geological visualisations, enhancing understanding of hydrology and contaminant transport, improving efficiencies and workflows, and eliminating travel time and costs. This innovation is critical to WSP’s future success in presenting hydrogeologic and contaminant data and conceptual site models.
”We were able to perform a mass calculation using the solids from the 3D model, which enabled us to significantly reduce the expected disposal costs said Tobias.
Creating 3D images of groundwater systems to replenish aquifers
Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR), which involves capturing surface water to replenish aquifers, is a crucial method for developing sustainable water resources for irrigation and potable supply.
Professor Rosemary Knight, from Stanford University’s Department of Geophysics, employs airborne electromagnetic surveys (AEM) to create 3D images of groundwater systems – akin to an MRI of the earth’s subsurface.
In California’s Central Valley, where groundwater is extensively pumped for irrigation, AEM has been instrumental in identifying areas best suited for MAR. This innovative approach is gaining traction globally, from California to Catalonia to India.
Site assessment and remediation
Infrastructure mega projects are highly complex, transformative, high-profile and high-cost. According to Krom, these projects necessitate detailed site and environmental risk assessments before any construction or excavation begins. This ensures the project’s impact on aquifer systems and groundwater provision is understood, and any ground contamination is identified and remediated.
The Lieberman Engineering Company, contracted by SAGA Group for a housing project in Hamburg, Germany, exemplifies this process.The site, formerly a school and adjacent landfill site, is being redeveloped into 211 flats to address the city’s housing needs. . Lieberman used Leapfrog Works to produce a 3D model of the site to communicate and visualise the contaminated land.
By integrating 3D models of the contaminant zones with the geological data and proposed site excavations, the Leapfrog Works model accurately determined the volumes of earth and materials to be moved or removed along with their different contamination levels. This helped identify reusable materials and how it needed to be handled safely. The 3D model also facilitated compliance with German Regulations.
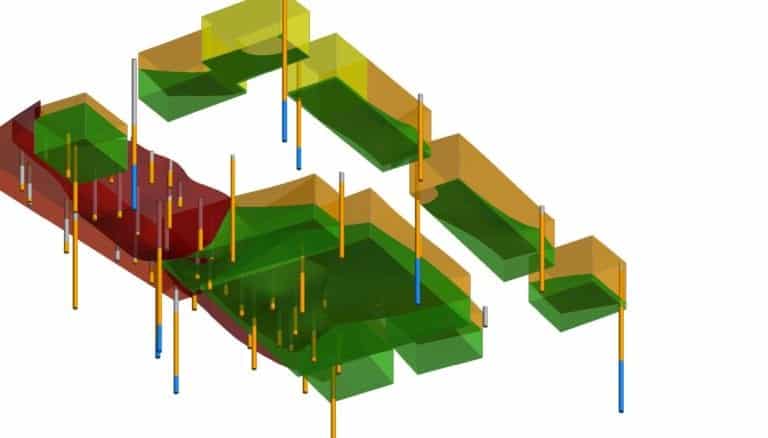
This view looking up from underneath the site shows the relationship of borehole depths to excavation areas.
High productivity tools sees up to 70% time savings
As the race to find and preserve groundwater resources intensifies and infrastructure demands necessitate quicker, robust decision-making, the ability to reach consensus swiftly on brownfield or contaminated sites and understand environmental impacts becomes paramount. Technology that simplifies the visualisation and comprehension of subsurface risks, making data more accessible, will enable faster interpretation, leading to significant time savings and greater efficiencies.
“Our customers tell us that they save a massive amount of time on projects, often 70% savings are seen due to the high productivity delivered by Seequent products,” says Krom. “Great technology acts as an enabler to projects looking to unlock the value of the data they have for greater insight and better outcomes.”





